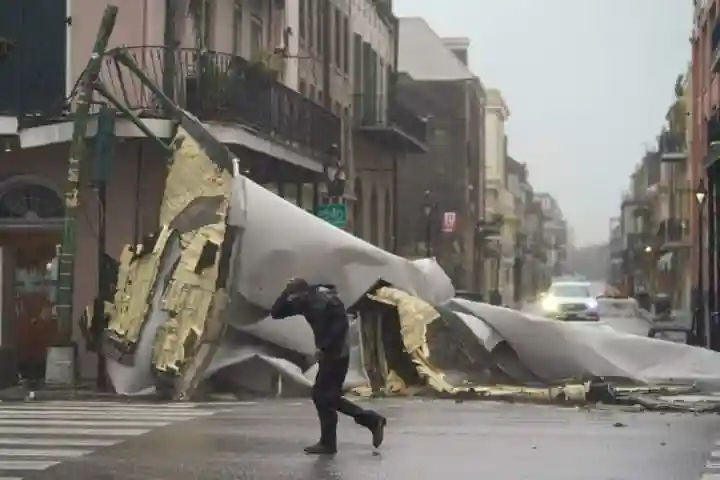

Devastation caused by the hurricane Ida which was a result of climate change (Pic. Courtesy Twitter/@weatherchannel)
<p>
The number of natural disasters, such as floods and heatwaves, caused by climate change have shot up fivefold over the past 50 years, killing more than 2 million people and resulting in economic losses to the tune of a phenomenal $3.64 trillion, according to a UN agency&rsquo;s report released on Wednesday.</p>
<p>
The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) claims its Atlas is the most comprehensive review of mortality and economic losses from weather, water and climate extremes ever compiled.</p>
<p>
It has studied around 11,000 disasters occurring between 1970-2019, including major catastrophes such as Ethiopia&#39;s 1983 drought, which was the single most fatal event with 300,000 deaths, and Hurricane Katrina in 2005 that caused the highest economic damage of a whopping $163.6 billion.</p>
<p>
The WMO hopes the report, which gives a detailed regional breakdown, will be used to help governments develop policies to better protect people.</p>
<p>
The WMO report attributed the growing frequency to both climate change and improved disaster reporting. The report comes just days after Category 4 hurricane Ida devastated southern Louisiana in the USA.</p>
<p>
&quot;Thanks to our early warning service improvement we have been able to have a decrease of the casualties at these kind of events, but the bad news is that the economic losses have been growing very rapidly and this growth is supposed to continue,&quot; WMO Secretary-General Petteri Taalas said at a press conference in Geneva.</p>
<p>
He forecast a gloomy scenario ahead, saying, &quot;this negative trend in climate will continue for the coming decades.&quot;</p>
<p>
The report showed an accelerating trend, with the number of disasters increasing nearly fivefold from the 1970s to the most recent decade, adding to signs that extreme weather events are becoming more frequent due to global warming.</p>
<p>
Costs from the events also surged from $175.4 billion in the 1970s to $1.38 trillion in the 2010s when storms such as Harvey, Maria and Irma ripped through the United States.</p>
<p>
But while hazards became more costly and frequent, the annual death toll has fallen from more than 50,000 in the 1970s to around 18,000 in the 2010s, suggesting that better planning was paying off.</p>
<p>
More than 91% of the 2 million deaths occurred in developing countries, the report said, noting that only half of the WMO&#39;s 193 members have multi-hazard early warning systems.</p>
<p>
It also said that &quot;severe gaps&quot; in weather observations, especially in Africa, were undermining the accuracy of early warning systems.&nbsp; It identified these countries as in need of help from the advanced nations to be better prepared for the future.</p>
<p>
<strong>Also read: <a href="https://www.indianarrative.com/science-news/rising-sea-may-submerge-mumbai-s-iconic-nariman-point-cuffe-parade-areas-by-says-top-official-111113.html">Rising sea may submerge Mumbai&rsquo;s iconic Nariman Point, Cuffe Parade areas by 2050, says top official</a></strong></p>
The Russian military has carried out a series of strikes on Ukrainian military-related targets in…
India's toy industry, once heavily dependent on imports, is now manufacturing domestically and exporting to…
Members of the Indian diaspora and several artists in Argentina welcomed Prime Minister Narendra Modi…
Sub Lieutenant Astha Poonia officially became the first woman to be streamed into the fighter…
As Israel awaits Hamas's response on Friday to the latest proposal for a hostage release…
Deputy Chief of Army Staff (Capability Development and Sustenance), Lieutenant General Rahul R Singh, on…