India’s big plan of unlocking the transport and logistics potential of the Eurasian region through the International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC) has received a push with the visit of Indian exporters to Russia’s Astrakhan region this week.
Indian Ambassador to Moscow Pavan Kapoor led the business-to-business (B2B) delegation’s trip mounted by the Federation of Indian Export Organisations (FIEO) at the invitation of Astrakhan Governor Igor Yuryevich Babushkin.
Babushkin held talks with the Indian delegation led by Ambassador Kapoor on Thursday, discussing in detail issues of further cooperation, including an increase in the transshipment of goods through Astrakhan ports in both directions.
On Friday, Kapoor, along with the visiting Indians, visited Lotus Special Economic Zone (SEZ) just north of Astrakhan which could play a major role in the development of cargo transportation via the INSTC – the 7200 km-long multimodal trade corridor which will start from Mumbai, with nodes in West Asia, Central Asia, Caucasia, and Russia covering large swathes of territory in the landlocked region.
Visited Lotus SEZ, just north of Astrakhan. Several enterprises engaged in activities ranging from Shipbuilding to textiles for road building, are already benefiting from infra & other support of the Govt. Indian companies could also evaluate this option. pic.twitter.com/JICivJRuto
— Amb Pavan Kapoor (@AmbKapoor) April 28, 2023
Located in the southeast of the European part of Russia, in the lower reaches of the Volga River, Astrakhan is not only rich in agriculture but also plays a critical role in logistics as it is washed by the Caspian Sea.
The region is part of the Russian Southern Federal District and is a border region: by land, its territory borders with Kazakhstan, and by sea with Azerbaijan, Iran, Kazakhstan, and Turkmenistan.
The Lower Volga region has been the center of Russian shipbuilding for several centuries and the industry is one of the most important for the region.
India has been pushing extensively for the utilization of New Delhi-backed Chabahar port in Iran, and its inclusion in the INSTC framework, since it will provide a great option to replace the Suez Canal with a massive reduction in travel time and savings.
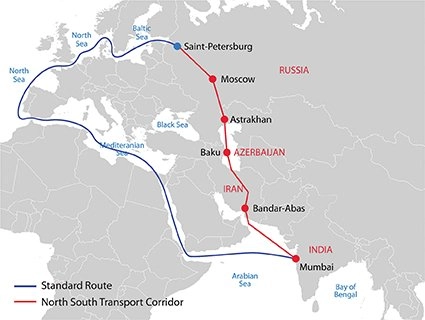
Currently, the lack of regular shipping lines between Russia and Iran as well as between Iran and India impedes the full-scale launch of the INSTC.
Russian President Vladimir Putin has highlighted active developments in Kazakhstan and Azerbaijan to advance the transport artery, emphasising that Moscow too continues to make “energetic efforts” in implementing the Strategy for the Development of National Seaports in the Caspian Basin, as well as rail and road approaches to them until 2030.
In his meeting with the Indian Ambassador, Babushkin stated that the number of deliveries of Russian goods to India through Astrakhan ports has increased markedly with paper, lumber, aluminum, Belarusian potash fertilizers, and other products reaching the Indian markets.
“We receive loads of Indian tea, peanuts, rice, and onions. Of course, we need to develop cooperation. He suggested that Indian companies consider the possibility of investing in the infrastructure of our port zone and opening production facilities in the Lotus SEZ. In particular, there could be located enterprises for the packaging of Indian products and the production of pharmaceutical products,” said the Astrakhan Governor.
He also stressed developing humanitarian ties – more than 50 students from India study at Astrakhan medical university – and invited Indian artists to participate in the international festival of classical music, which will be held in September.
“We will make every effort to further strengthen our friendly ties,” said Babushkin.

As he discussed opportunities for economic cooperation in diverse areas, Ambassador Kapoor too recalled the historic association of the city with Indian traders going back to the 17th century and more recent links with Gujarat.
Astrakhan is the first place in Russia where an Indian merchant colony was established as early as the 1630s. An Indian trade house was constructed with about 70 shops as trade between India and Russia through Astrakhan was considered so important that the Russian Tsar (on May 20, 1647) issued a decree guaranteeing the personal and material safety of Indians in Russia, reaffirmed by Peter the Great in 1722.
According to the documents of the Astrakhan Customs of 1773, Indian merchants imported mostly silk and textiles, jewels, pearls, rice, incense, and spices. Such business contacts slowly developed into stronger relationships and Indians were assimilated into the society by way of marriages. The two-storey building that was a part of the Indian trade house still exists in Astrakhan.

Just after the North-South Corridor Project Agreement was signed between India, Iran and Russia in September 2000, PM Modi, then Gujarat Chief Minister, had signed a cooperation agreement between the state and the Astrakhan region to bring closer not only the two regions but also the two countries by way of enhanced trade, joint projects and other forms of economic exchanges.
In June 2017, while interacting with 16 Governors of various provinces of Russia, PM Modi recalled warmly his visit to Astrakhan in 2001 as Chief Minister of Gujarat and reiterated his vision that relationships between regions and provinces of two countries are a vital part of nurturing the bilateral relationship.




















