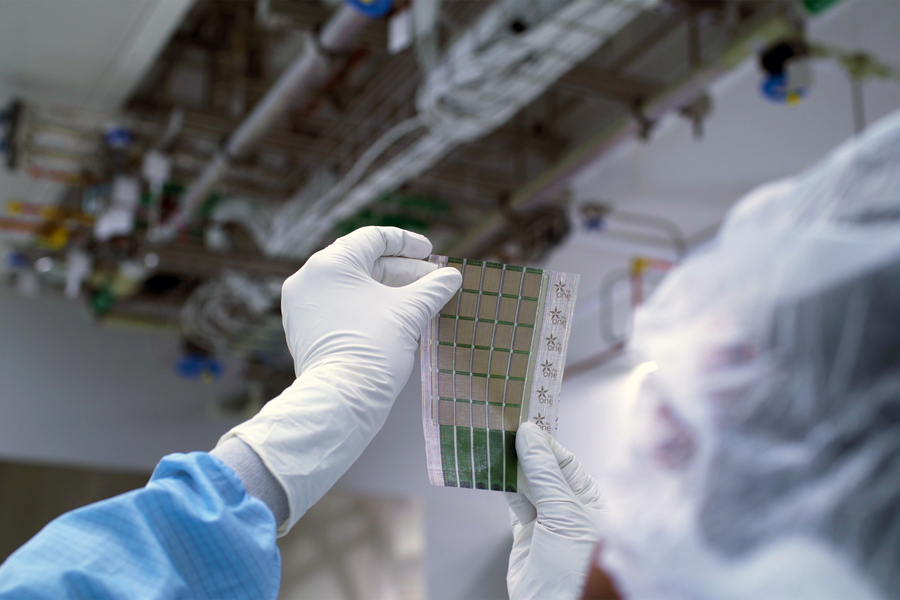

MIT engineers have developed ultralight fabric solar cells that can quickly and easily turn any surface into a power source.
MIT (Massachusetts Institute of Technology) engineers have developed ultralight fabric solar cells that can quickly and easily turn any surface into a power source.
These durable, flexible solar cells, which are much thinner than a human hair, are glued to a strong, lightweight fabric, making them easy to install on a fixed surface. They can provide energy on the go as a wearable power fabric or be transported and rapidly deployed in remote locations for assistance in emergencies, according to a report published in MIT News.
They are one-hundredth the weight of conventional solar panels, generate 18 times more power-per-kilogram, and are made from semiconducting inks using printing processes that can be scaled in the future to large-area manufacturing.
Because they are so thin and lightweight, these solar cells can be laminated onto many different surfaces. For instance, they could be integrated onto the sails of a boat to provide power while at sea, adhered onto tents and tarps that are deployed in disaster recovery operations, or applied onto the wings of drones to extend their flying range. This lightweight solar technology can be easily integrated into built environments with minimal installation needs, the report states.
“The metrics used to evaluate a new solar cell technology are typically limited to their power conversion efficiency and their cost in dollars-per-watt. Just as important is integrability — the ease with which the new technology can be adapted. The lightweight solar fabrics enable integrability, providing impetus for the current work. We strive to accelerate solar adoption, given the present urgent need to deploy new carbon-free sources of energy,” says Vladimir Bulović, the Fariborz Maseeh Chair in Emerging Technology, leader of the Organic and Nanostructured Electronics Laboratory (ONE Lab), director of MIT.nano, and senior author of a new paper describing the work.
Joining Bulović on the paper are co-lead authors Mayuran Saravanapavanantham, an electrical engineering and computer science graduate student at MIT; and Jeremiah Mwaura, a research scientist in the MIT Research Laboratory of Electronics. The research was published on December 9 in Small Methods.
Union Minister of Coal and Mines G Kishan Reddy on Tuesday held an inter-ministerial meeting…
India's largest automobile in-plant railway siding at Maruti Suzuki's Manesar facility started operation on Tuesday,…
Google on Tuesday unveiled its Safety Charter for India's AI-led transformation, at the "Safer with…
The human rights organisation of the Baloch National Movement (BNM), Paank, has published its most…
The Israel Defence Forces (IDF) on Tuesday claimed that it has killed Iran's senior-most military…
Amid escalating conflict between Iran and Israel, the Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) on Tuesday…