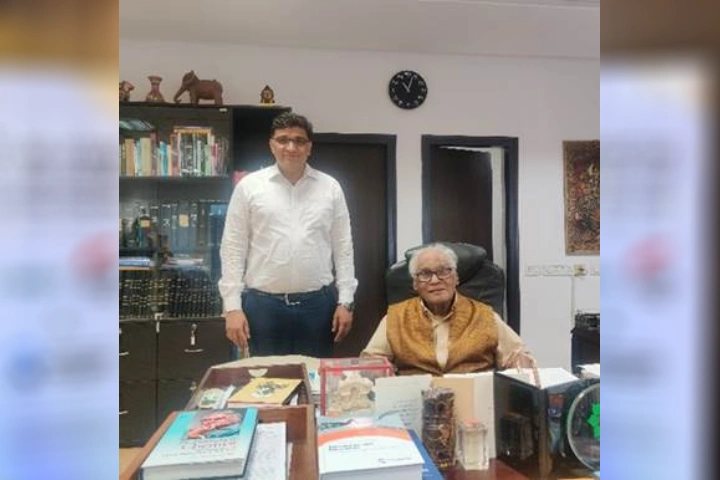

Prof. Vishnoi and Prof. CNR Rao (Image: PIB)
A team of Indian scientists has explored precise atomic rearrangements that occur in each phase transition of lead iodide perovskites due to altered temperature and pressure and their resulting effects on optoelectronic properties that could help in efficient renewable energy generation, the Union Science & Technology Ministry said on Monday.
In a new study published in the Royal Society of Chemistry’s Journal of Materials Chemistry A, Professor Pratap Vishnoi and Professor C.N.R. Rao from Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research (JNCASR), Bengaluru (an autonomous institution under the Department of Science & Technology), have reviewed the current knowledge gaps and recent progress on hybrid lead iodide perovskites.
In recent years, lead iodide perovskites have attracted much attention.
While their energy conversion efficiency can be higher than even that of commercial silicon-based solar cells, the scientists said that lead iodide perovskites are not inherently stable materials.
Studies have reported that these materials undergo different structural changes (or ‘phase transitions’) even under similar conditions. Temperature and pressure shifts can easily modify their crystalline structure, altering their physical properties and lowering their performance.
The researchers reviewed over a hundred publications of existing literature on the reported phase transitions and crystal structures.
They focused on the results of these studies and the experimental methodologies used by their authors. This approach highlighted the strengths and limitations of the commonly employed techniques, such as X-ray and neutron diffraction.
The researchers also touched on the topic of chemical instability in lead iodide perovskites, specifically, how and why these materials decompose when exposed to humid air.
As per researchers, further studies on lead iodide perovskites, as well as other types of hybrid perovskites, will hopefully lead to more efficient renewable energy generation.
If their instability problems can be efficiently addressed, they could make for great materials for solar cells, since they can be processed into thin films, the researchers said.
Israel Defence Forces Spokesperson Brigadier General Effie Defrin on Thursday said that Iran has expressed…
India's Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) and French engine manufacturer, Safran Aircraft Engines, signed an agreement…
India has emerged as a country with the third-largest growth in power generation capacity globally…
Prime Minister Narendra Modi hailed Indian chess grandmaster Divya Deshmukh for defeating world number one…
The family of detained Baloch leader Mahrang Baloch has accused prison authorities at Quetta's Hudda…
The QS World University 2026 Rankings bring great news for our education sector, as the…