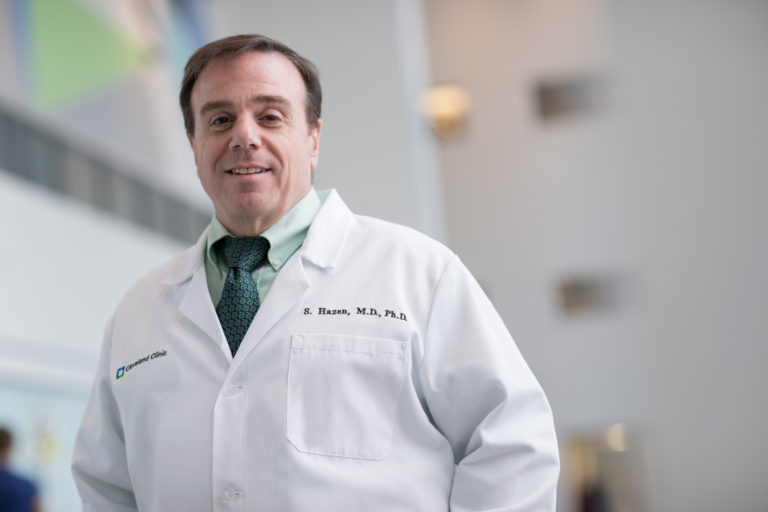

Stanley Hazen, M.D., Ph.D.
New research carried out by the prestigious Cleveland Clinic shows that erythritol, a popular artificial sweetener, is associated with an increased risk of heart attack and stroke. The findings were published on Feb 27 in Nature Medicine.
Researchers studied over 4,000 people in the U.S. and Europe and found those with higher blood erythritol levels were at higher risk of experiencing a major adverse cardiac event such as heart attack, stroke or death, according to a statement on the Cleveland Clinic website.
The researchers also examined the effects of adding erythritol to either whole blood or isolated platelets, which are cell fragments that clump together to stop bleeding and contribute to blood clots. Results revealed that erythritol made platelets easier to activate and form a clot. Pre-clinical studies confirmed ingestion of erythritol heightened clot formation.
“Sweeteners like erythritol, have rapidly increased in popularity in recent years but there needs to be more in-depth research into their long-term effects,” said senior author Stanley Hazen, M.D., Ph.D., chairman for the Department of Cardiovascular & Metabolic Sciences in Lerner Research Institute and co-section head of Preventive Cardiology at Cleveland Clinic.
Artificial sweeteners, such as erythritol, are common replacements for table sugar in low-calorie, low-carbohydrate and “keto” products. Sugar-free products containing erythritol are often recommended for people who have obesity, diabetes or metabolic syndrome and are looking for options to help manage their sugar or calorie intake. People with these conditions also are at higher risk for adverse cardiovascular events like heart attack and stroke.
Erythritol is about 70% as sweet as sugar and is produced through fermenting corn. After ingestion, erythritol is poorly metabolized by the body. Instead, it goes into the bloodstream and leaves the body mainly through urine. The human body creates low amounts of erythritol naturally, so any additional consumption can accumulate, the study points out.
Measuring artificial sweeteners is difficult and labeling requirements are minimal and often do not list individual compounds. Erythritol is “Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS)” by the FDA, which means there is no requirement for long-term safety studies.
“Our study shows that when participants consumed an artificially sweetened beverage with an amount of erythritol found in many processed foods, markedly elevated levels in the blood are observed for days – levels well above those observed to enhance clotting risks,” said Dr. Hazen.
The authors recommend talking to your doctor or a certified dietician to learn more about healthy food choices and for personalized recommendations.
The United Kashmir People's National Party (UKPNP) held a demonstration outside the United Nations headquarters…
President William Lai has discussed how pro-Taiwan and pro-China groups can agree to maintain solidarity…
Union Minister Jitendra Singh on Wednesday hailed Prime Minister Narendra Modi's decision to open up…
Tibetan Government-in-Exile President Sikyong Penpa Tsering concluded a significant three-day official visit to the UK…
By Amrit Prakash India unveiled its first Advanced Traffic Management System (ATMS) project at Delhi's…
The Indian Armed Forces actively participated in the ongoing multinational exercise 'Khaan Quest 2025' at…