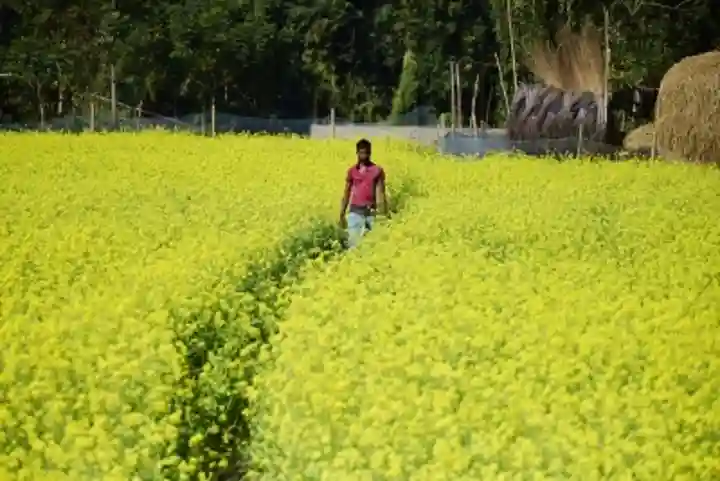

India's food prices easing rapidly
The ban on foodgrain exports which include rice and wheat is set to continue for long as India looks to prioritise its domestic needs. Not just that. The government is looking at a fool proof mechanism to address any future food shocks that may arise from external factors or climate change.
Amid the ongoing Russia-Ukraine war which has had a severe impact on food and energy sectors, India which experienced untimely rains in the last two months was in the grip of an intense heat wave in May. Besides, the beginning of the monsoon season was also marked by patchy rains.
“We are not against exports of foodgrains but the domestic market comes first and until the global uncertainties are settled — which do not look like easing anytime soon, the government will not be comfortable with outbound shipment of rice or other essential food items,” a person in the know told India Narrative.
Driven by high energy and fertiliser prices globally along with untimely rains that caused damage to the Kharif crops, the cost of food in India increased 8.6 per cent year-on-year in September — the biggest rate since November 2020. Vegetables prices increased by more than 18 per cent while cereals recorded an 11.53 per cent jump.
Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman, speaking at a session at Brookings Institution said that food security is a cause for concern.
“Some parts of the country are in severe food insecurity due to external factors,” she said.
The Observer Research Foundation has recommended increasing public spending on agriculture adaptation measures. “Public investment in agricultural research, irrigation, extension services, and climate-smart agricultural practices should be increased. Given that the climate crisis will adversely affect the ability of the poor to access food through income losses, livelihood security provided by safety nets such as the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS) will become even more critical,” it said.
Meanwhile, amid rising concerns over climate change, India is expected to expand millets and millet flour in its public distribution system. The government has also decided to increase its focus on increasing millet production across the country, which will also help India in achieving its sustainable development goals (SDGs) including achieving zero hunger along with provision of nutritional food.
Also read: “A logistical marvel” says IMF on India’s direct cash transfer scheme
Prime Minister Narendra Modi interacted with members of the Indian diaspora here on Wednesday as…
The city of Hamburg in Germany is set to host the 11th edition of India…
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) has confirmed that two Iranian centrifuge production facilities, TESA…
The human rights department of the Baloch National Movement (BNM), Paank, has strongly condemned the…
In a major boost to India's coastal defence capabilities, the Indian Navy on Wednesday commissioned…
Volker Turk, the UN High Commissioner for Human Rights, on June 17 expressed concern over…